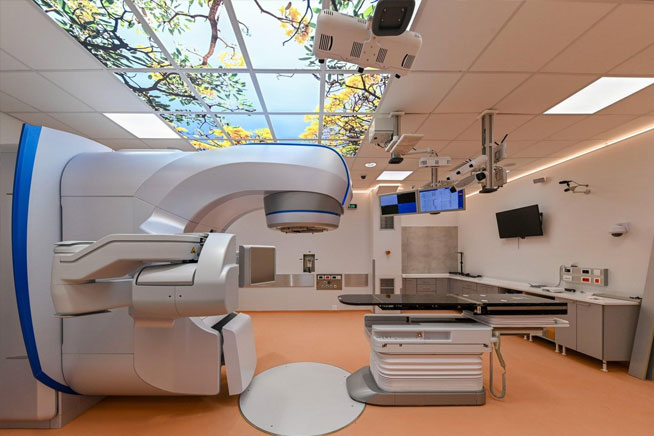
Radiation Oncology is a medical specialty that focuses on the use of ionizing radiation to treat and manage cancer. This branch of medicine plays a crucial role in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer care, working alongside surgical oncologists, medical oncologists, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive cancer treatment. Here are key details about Radiation Oncology:
Role of a Radiation Oncologist:
Treatment Planning:
- Radiation oncologists are responsible for creating personalized treatment plans based on the type, location, and stage of cancer.
- They work closely with medical physicists and dosimetrists to determine the optimal dosage and delivery of radiation.
Radiation Therapy Administration:
- Radiation therapy is delivered using various techniques, such as external beam radiation (from outside the body) or brachytherapy (placing radiation sources directly into or near the tumor).
- The goal is to destroy or damage cancer cells while minimizing harm to surrounding healthy tissues.
Coordination with Other Specialists:
- Radiation oncologists collaborate with surgical and medical oncologists, as well as other specialists, to ensure a comprehensive and effective treatment approach.
- Multidisciplinary tumor boards are often convened to discuss complex cases and determine the best course of action.
Types of Radiation Therapy:
External Beam Radiation:
- Most common form of radiation therapy.
- Involves directing high-energy beams from a machine outside the body toward the tumor.
Brachytherapy:
- Involves placing radioactive sources directly inside or very close to the tumor.
- Commonly used for certain types of cancers, such as prostate, cervical, and breast cancers.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT):
- Precise delivery of a highly focused dose of radiation to a specific target.
- Used for tumors in the brain (SRS) or throughout the body (SBRT).
Responsibilities Beyond Treatment:
Patient Counseling:
- Radiation oncologists educate patients about their treatment options, potential side effects, and the expected outcomes.
Follow-Up Care:
- Monitor patients during and after treatment to assess response and manage any side effects.
- Provide long-term follow-up care to address survivorship issues and potential recurrence.
Technological Advancements:
Advanced Imaging:
- Integration of advanced imaging techniques (such as CT, MRI, and PET scans) for precise treatment planning.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT):
- Techniques that optimize the delivery of radiation, allowing for increased precision and reduced impact on surrounding healthy tissues.
Proton Therapy:
- Utilizes protons instead of traditional X-rays, providing a more targeted dose to the tumor with less damage to nearby tissues.
Radiation Oncology plays a crucial role in cancer treatment, offering curative or palliative options depending on the nature of the disease. The field continually evolves with advancements in technology and treatment strategies, aiming to improve outcomes and minimize treatment-related side effects.

