Understanding Lung Cancer: Unveiling the Challenges and Hope for Tomorrow
Lung cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, arises when abnormal cells in the lungs multiply uncontrollably. Comprehending the key aspects of lung cancer, from risk factors to detection and treatment, is vital in the collective effort to combat this formidable disease.
Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to the risk of developing lung cancer, including:
- Smoking: The most significant risk factor; both active and passive smoking increase susceptibility.
- Exposure to Radon Gas: A naturally occurring gas that can accumulate in homes.
- Occupational Exposures: Asbestos, arsenic, and certain chemicals increase risk.
- Family History: A familial predisposition may elevate the likelihood.
Types of Lung Cancer:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, comprising adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): More aggressive and often associated with extensive smoking.
Symptoms:
Early-stage lung cancer may not exhibit noticeable symptoms, but as the disease progresses, common signs include:
- Persistent Cough: Especially if accompanied by blood.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unintended weight loss.
Screening and Diagnosis:
- Imaging Tests: Chest X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to visualize lung abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Tissue sampling for laboratory analysis confirms the presence of cancer.
- Sputum Cytology: Examination of coughed-up mucus for cancer cells.
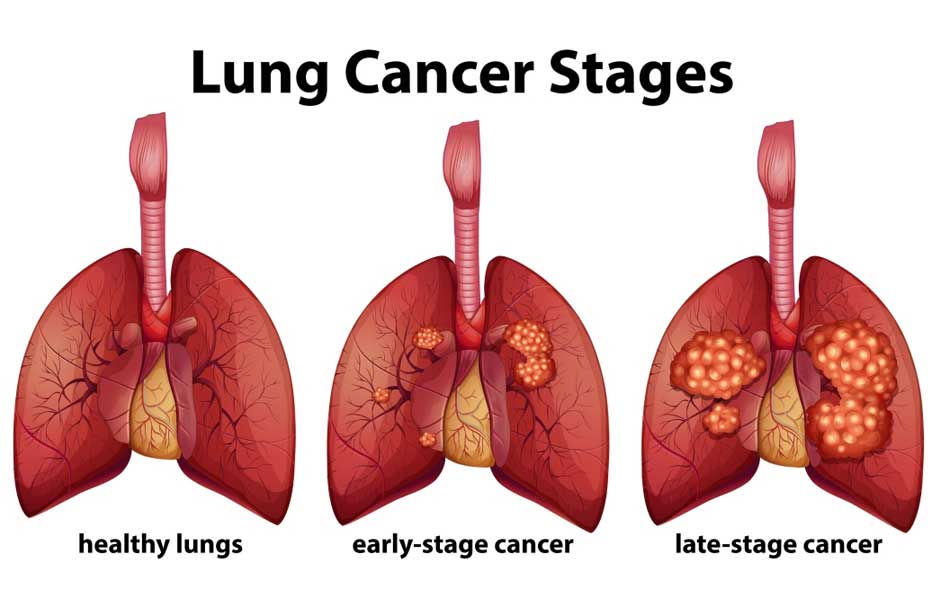
Stages:
Lung cancer staging determines the extent of disease progression:
- Stage I and II: Limited to the lungs with varying tumor sizes.
- Stage III: Locally advanced with lymph node involvement.
- Stage IV: Advanced cancer that has spread to other organs.
Treatment Options:
Treatment plans are personalized based on cancer type, stage, and individual factors:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor, lobectomy, pneumonectomy, or wedge resection.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to eliminate cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications to destroy or control cancer cells throughout the body.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Survivorship and Support:
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: Regular check-ups and imaging to monitor for recurrence.
- Palliative Care: To manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Support Groups: Emotional support through sharing experiences.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle for overall well-being.
Prevention:
While not all lung cancers can be prevented, certain measures may reduce risk:
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking significantly lowers the risk.
- Radon Mitigation: Testing and mitigating radon exposure in homes.
- Occupational Safety: Minimizing exposure to workplace carcinogens.
Conclusion:
Lung cancer presents formidable challenges, but advancements in research and treatment provide hope. Awareness, early detection, and ongoing research efforts are essential in the collective fight against lung cancer. If you experience symptoms or fall within high-risk categories, seeking prompt medical evaluation is crucial for timely intervention and care.

