
Cancer, a complex and multifaceted disease, affects millions of people worldwide. With over 100 different types, cancer arises when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, invading and damaging tissues and organs. In this blog, we'll explore the most common types of cancer, their symptoms, risk factors, and potential prevention strategies.
1. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women globally. It originates in the breast tissues, typically in the ducts or lobules. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Symptoms: Lumps in the breast, changes in breast shape or size, skin dimpling, nipple discharge, and redness.
Risk Factors: Age, family history, genetic mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2), hormone replacement therapy, and lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption and obesity.
Prevention: Regular mammograms, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, limiting alcohol intake, and considering genetic testing if there's a family history.
2. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, primarily affects smokers. However, non-smokers are also at risk due to factors like secondhand smoke and environmental pollutants.
Symptoms: Persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, shortness of breath, and recurrent respiratory infections.
Risk Factors: Smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution.
Prevention: Quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, testing homes for radon, and using protective gear in environments with harmful substances.
3. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men, particularly affecting older males. It develops in the prostate gland, which is responsible for producing seminal fluid.
Symptoms: Difficulty urinating, decreased urine flow, blood in urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and pelvic discomfort.
Risk Factors: Age, family history, race (more common in African-American men), and dietary factors.
Prevention: Regular screenings, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and staying physically active.
4. Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer affects the colon or rectum and is the third most common cancer worldwide. Early detection through screening is vital for effective treatment.
Symptoms: Changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, abdominal discomfort, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
Risk Factors: Age, family history, inflammatory bowel disease, a diet high in red and processed meats, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Prevention: Regular screenings (colonoscopy), a diet high in fiber, maintaining a healthy weight, and exercising regularly.
5. Skin Cancer
Skin cancer, including melanoma and non-melanoma types (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma), is the most common type of cancer in the United States. It is primarily caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
Symptoms: New or changing moles, unusual skin growths, sores that don't heal, and changes in skin color or texture.
Risk Factors: UV radiation exposure, fair skin, a history of sunburns, numerous moles, and a family history of skin cancer.
Prevention: Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, avoiding tanning beds, and performing regular skin self-exams.
6. Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer typically begins in the cells lining the bladder. It is more common in men and older adults.
Symptoms: Blood in urine, frequent urination, painful urination, and lower back pain.
Risk Factors: Smoking, exposure to certain industrial chemicals, chronic bladder inflammation, and a family history of bladder cancer.
Prevention: Quitting smoking, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals, drinking plenty of fluids, and regular medical check-ups if at risk.
7. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a type of cancer that begins in the lymphatic system. It can occur at any age but is more common in older adults.
Symptoms: Swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
Risk Factors: Weakened immune system, certain infections (such as HIV or Epstein-Barr virus), exposure to chemicals like pesticides, and age.
Prevention: There are no guaranteed prevention methods, but maintaining a healthy immune system, avoiding exposure to known risk factors, and regular medical check-ups can help in early detection.
8. Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, often goes undetected until it has progressed significantly. It begins in the kidneys, which filter waste from the blood.
Symptoms: Blood in urine, a lump or pain in the side or back, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
Risk Factors: Smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, family history, and certain genetic conditions.
Prevention: Maintaining a healthy weight, controlling blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Conclusion
Understanding the most common types of cancer and their associated risk factors is essential for early detection and prevention. Regular screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of symptoms can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and screening recommendations. By taking proactive steps, we can better manage our health and potentially prevent the onset of this formidable disease.
Latest Blogs
-

-
10 Questions to Ask Your Cancer Surgeon Before Surgery
21 August, Admin
-

-
Knowing These 6 Signs of Throat Cancer Can Save Your Life
27 July, Admin
-
-
How Jaipur’s Best Cancer Surgeons Are Changing Lives
18 July, Admin
-

-
How Do I Choose A Cancer Hospital For Treatment?
08 July, Admin
-
-
Bridging Hope: How a Cancer Surgeon Changes Lives
29 June, Admin
-

-
Symptoms of Neck and Head Cancer
11 June, Admin
-

-
When Is the Best Time to Visit a Cancer Hospital in India
30 May, Admin
-

-
Understanding the Most Common Types of Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
16 May, Admin
-

-
Lifestyle Risk Factors of Cancer
19 January, By Admin
-
-
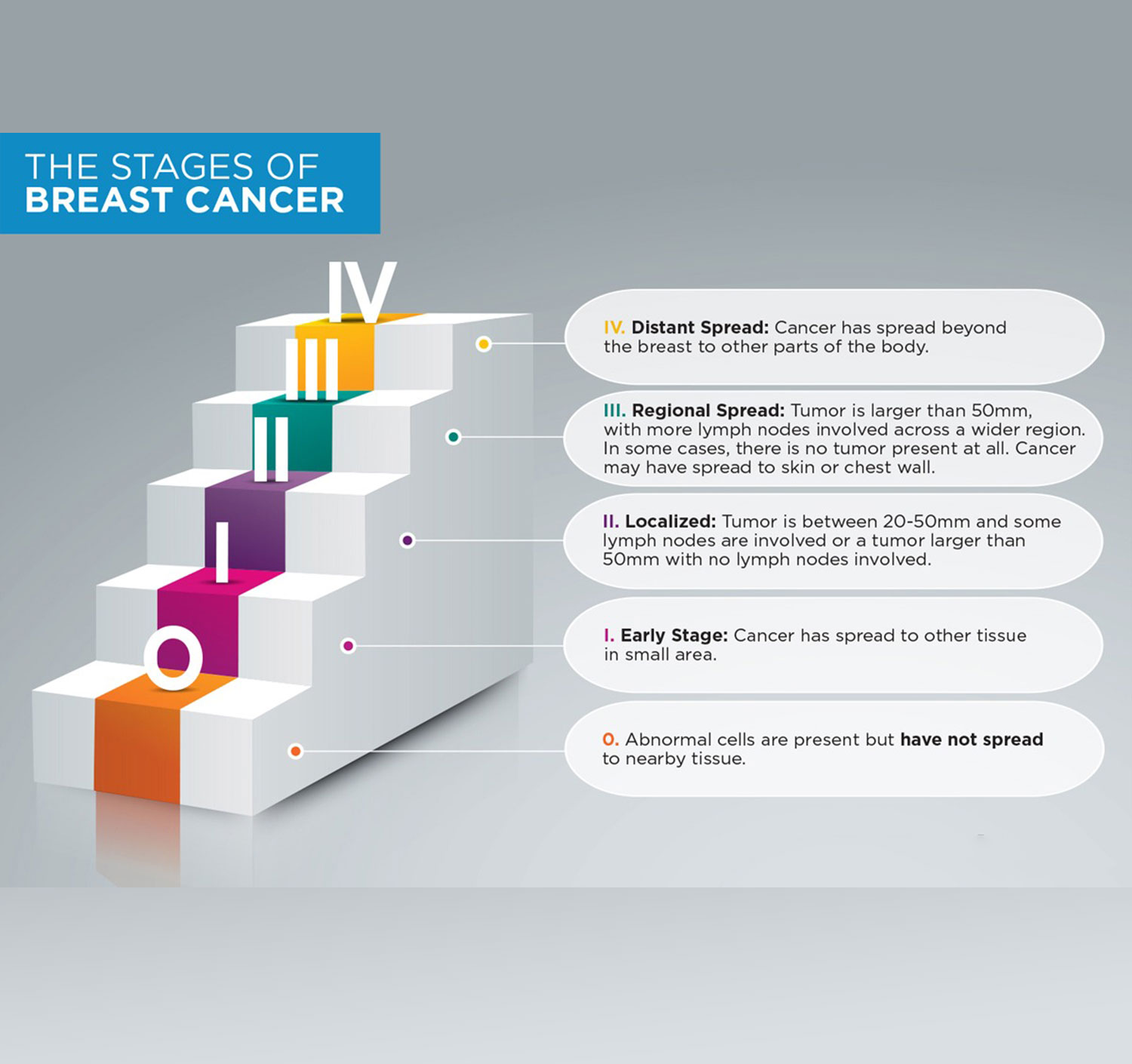
The Stages of Breast Cancer
19 January, By Admin

